CASTOR: Challenges & Opportunities of 3D Printing for the Oil and Gas Industry
https://www.3dcastor.com/post/challenges-opportunities-of-3d-printing-for-the-oil-and-gas-industry
For over a century, the oil and gas industry has driven many of the industrial innovations that have taken place around the world. According to research, the oil and gas industry is estimated to be ~$210B and supplies some ~10M jobs just in the United States.
When we look at the adoption of Additive Manufacturing, the oil and gas industry has yet to realize its true potential, and it has been growing comparatively slower than other industries. However, with the industry facing challenges from oil price volatility and a shift towards alternative energy sources, it is increasingly becoming essential for stakeholders to reduce operational costs, and they are searching for innovative solutions to tackle this challenge
Along with the demand for this Energy as a commodity that is never seeming to dip, innovative companies, both large and small, are looking at 3D Printing in the energy, oil, and gas industry as the next big manufacturing innovation to drive the industry into the future.
Common Examples of 3D Printing in the Oil and Gas Industry
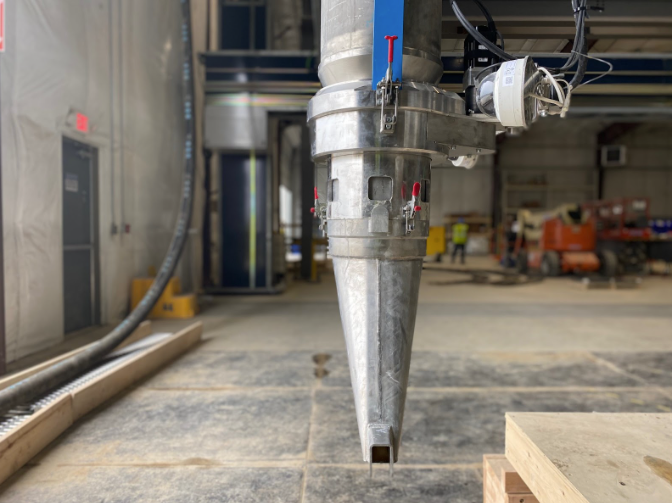
Production of drilling tools:
Additive manufacturing is being used to produce stabilizers, drill bits, and other downhole tools for oil and gas exploration and production.
Replacement parts:
3D printing in the oil and gas sector can also manufacture replacement parts for valves, pumps, and other equipment that are no longer available or difficult to source, reducing the requirement of expensive repairs.
Customized pipeline components:
The technology is beneficial in producing customized pipeline components, including fittings, flangers, and connectors. These can be manufactured on demand while being customized to specific applications, thereby boosting performance and reducing lead times.

The Challenges of Adopting Additive Manufacturing in the Oil and Gas Industry
While 3D Printing could be a useful addition compared to traditional manufacturing methods, the adoption of the technology involves some hurdles for oil and gas companies.
Material Composition Standards
The oil and gas industry operates in harsh environments with high pressures, high temperatures, and corrosive substances, all materials used must be compatible with these conditions. While there are several options for 3D printing materials, including metal and polymer, not all materials are suitable for these harsh environments.
Governance & Regulatory Requirements
The oil and gas industry involves numerous governing bodies that set standards for the entire supply chain within the energy sector, such as the American Petroleum Institute (API). Those can hinder the adoption of 3D Printing in oil, gas & renewable energy sectors.

Additive Manufacturing is a rather new technology that is going through a fast research and development cycle. The adoption process of 3D printing is often slow, requiring an immense amount of Engineering know-how to get things operational.
How Additive Manufacturing Can Overcome these challenges
Overwhelmingly, the oil and gas industry is (and has been) at an inflection point.
It utilizes 3D printing to make parts that are complex in shape and cheap, such as spares and replacements. There are various advantages that the technology offers over conventional subtractive manufacturing. Aside from part consolidation, circular supply chain, improved quality control and a number of other benefits, Additive Manufacturing finds itself integral in a number of ways in the oil and gas industry. Continue on to learn more about some of these applications and the tangible benefits 3D Printing offers.
On-Demand Manufacturing
Oil and gas plants are spread all around the world, this means that the logistic efforts and costs are high. The high cost of downtime further exacerbates the difficulty with component supply. Most operators work to reduce unplanned downtime by keeping large inventories of vital spare parts, since creating high-quality parts for maintenance and repairs is necessary and adds expense to transportation and production.
There are numerous additive manufacturing techniques available to optimize asset maintenance. Industry leaders, suppliers, and maintenance companies are all pursuing additive manufacturing to do repairs faster and with higher design quality. 3D printing in the oil and gas industry uses on-demand printing to reduce warehouse inventories. Given the historical volatility of oil prices, the savings that follow are more significant. A large oil company like Shell or GE Oil have an array of 3D Printing applications just within the realm of offshore rigs, oil drills, and rapid prototyping. Many of these organizations use 3D Printing to maintain these rigs which contain pipes and transportation methods used for the global oil and gas industry,

Minimized transportation costs, enhanced design freedom, just-in-time manufacturing and more are just some of the reasons why we see an opportunity for 3D Printing to benefit the product development and overall manufacturing process within the oil and gas drilling industries. Using additive manufacturing, production costs can be decreased while lead times are shortened.
Enhanced Component Quality

In the case of GE Energy, their direct benefits related to 3D Printing come in the form of 3D Printed metal cement for gas turbines to increase wind farm efficiency. Not only is time savings a huge factor in this application, but material costs go down in addition to improved component integrity.
Complex Geometries
Some parts used in the oil and gas industry have complex geometries that are difficult to manufacture using traditional methods. 3D Printing allows for the creation of complex geometries that are precise and accurate. This 3D technology can be used to create parts suchas turbomachinery impellers, turbine blades & nozzles, and other complex shapes that are essential to energy manufacturing and alternative design. Additionally, the emergence of 3D Scanning technology has also assisted companies that are considering adopting 3D Printing. Product designers alike are quickly becoming aware of the benefits an additive manufacturing process can help with, especially for heavy manufacturing equipment, offshore drills, rigs, and other parts of the oil and gas industry.

Also, some techniques for additive manufacturing, like direct energy deposition, could be used to fix or remake old manufacturing equipment. By extending the lifespan and efficiency of worn-out and damaged components like valves, pumps, and shafts, the approach can reduce total operating and maintenance costs.
Innovating New Products

In 2016, Shell used 3D printing to make a successful prototype of an oil and gas drilling buoy. Traditional methods of making things would have taken months to make a working plastic prototype, but thanks to the technology, the experts were able to do this in just four weeks.

As additive manufacturing enables the creation of complicated components with greater performance, less weight, and increased durability, it has the potential to revolutionize the oil and gas industry. To increase the overall effectiveness of the industry, the sector must continue to create materials and procedures that work with additive manufacturing.
To summarize,
The use of additive manufacturing in the oil and gas industry might spread to regional hubs and offshore locations, revolutionizing supply chain processes. Over the next ten years, as new uses for 3D printing are found and new business opportunities with 3D printing materials and technology come up, the oil and gas industry will definitely see and take advantage of its benefits.