How CNC Machining Has Transformed Automation In The Manufacturing Industry
https://www.iaasiaonline.com/how-cnc-machining-has-transformed-automation-in-the-manufacturing-industry/
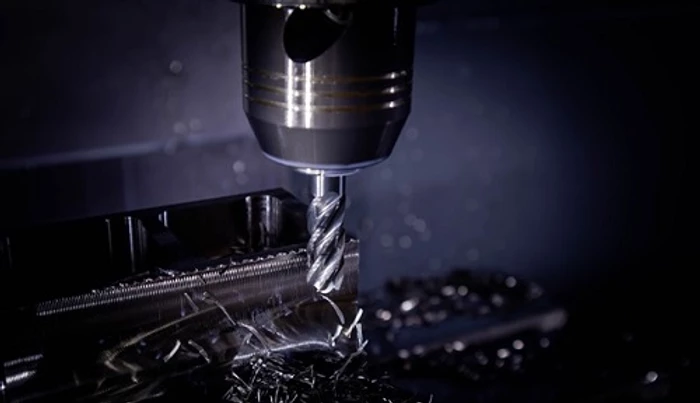
CNC machining has made revolutionary strides over the past few decades. What started as manual machining during the Industrial Revolution evolved into NC machining, and today it has become a fully automated, systematic manufacturing process found in virtually every country and industry.
Today’s high-volume, production-oriented machinery for CNC, injection molding, fabrication, and most other manufacturing methodologies is a highly sophisticated, automated system or processes working together in complete synchrony.
Improvements to the machining industry on a global scale have also allowed for the adoption of newer automation technologies that spill over into other industries such as injection molding.
Below are just a few of the ways automation has led to dramatic advancements in CNC machining.
Impact On Automation In Manufacturing
Without a doubt, the automation, robotics, and systems that have gone into CNC machining have made it the powerful, seamless, and highly precise process it is today.
Round-the-clock operation
Pallet-changing systems, milling machines, the internet of things (IoT), and a variety of other technologies have made it possible for the CNC process to run continuously, stopping only for routine or planned maintenance, part changeovers, or setups for new jobs.
Precision
Manual machining and other labor-intensive manufacturing methodologies have always been prone to human error, allowing for a lack of precision, lower yields, and less tolerancing and surface finish to be prevalent early on.
Since this process is now entirely computer or data driven, as long as the programmer and operator or technician is highly skilled, there is very little room for error, and it will almost always produce a repeatable, precise metal component.
Precision-ground ball screws have become increasingly accurate over the years, and servo systems have become repeatable, faster, and able to operate more efficiently.
The quality of machine tools and advancements in the coated inserts and CAT40/CAT50 tooling that holds these extremely hard and rigid cutting tools has also improved the overall quality of machining, plus it has allowed for a great surface finish.
Safety
Safety measures have evolved significantly over the years to answer the changing risks and demands of developing technology. Safety is naturally a priority for OEMs who design heavy, capital equipment.
Since many operations are automated, this allows most machines today to be enclosed—and for operators to remain clear of dangerous moving parts. A suite of sensors is in place to stop injuries and other damage from happening.
For example, a door safety switch on a machining center can automatically stop all machining operations to avoid moving spindles and flying metal chips while the operator has the doors open.
Speed
With faster automation hardware and metalworking components, the overall speed, throughput, and efficiency of the metalcutting, plastic injection molding, or virtually any motor-controlled manufacturing process has improved dramatically.
Some of the contributing factors are:
-
Higher-RPM spindles.
-
Faster ball screws and motor-driven systems that can feed various axes of milling or turning systems.
-
More powerful, accurate controls and software.
Thanks to automation, CNC machines are becoming faster every year, continually speeding up manufacturing.
Adaptability
CNC machines are known to be flexible in the types, quantities, materials, and designs they can handle. Whether it’s millions of nuts, bolts, and fasteners on a screw machine, tens of thousands of circular components made from fully automated turning centers, or batches of various high-mix, low-volume cycle runs with a milling machine, they can always handle the task.
From a workflow standpoint, a different array of machining or turning centers can be placed on the factory floor in ways that drive immense scale, minimal overhead, and maximum profitability.
The industry has also seen a number of workflow efficiency upgrades with the addition of robotics, including collaborative robots, also known as cobots. What robotics brings to the machine shop is the possibility of “lights-out,” round-the-clock machining.
CNC, injection molding, fabrication, and other industrial technologies can function without constant human involvement. This allows the human workforce to advance from repetitive, potentially dangerous tasks to taking on more technical, bigger-picture responsibilities.
Closing Remarks
Automation has driven improved efficiency in every element of the CNC design and manufacturing process. This includes CAD or CAM software that helps the designer optimize their digital design for proper design for manufacturability (DfM). For the machine tool, it’s a servo-driven drivetrain that is entirely automated, from raw material to finished metal piece of manufacturing art.
CNC machining has helped birth all sorts of manufacturing innovations, such as 3D printing, electrical discharge machining (EDM), hydrostatics, and other new forms of additive and subtractive manufacturing.
With each development comes new software, a faster motor, or more precise tooling that leads to improvements in efficiency in all adjacent technologies.